The Importance of Vision and Hearing Tests for Seniors
Aging is a natural part of life, but it brings a variety of changes that can impact day-to-day activities and overall quality of life. Among these changes, declining vision and hearing abilities are some of the most common and concerning. For seniors, regular vision and hearing tests are crucial for maintaining independence, safety, and emotional well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore why these tests matter, what they involve, and how they contribute to a healthier and more fulfilling life for older adults.
Why Vision and Hearing Matter as We Age
As we grow older, our bodies undergo numerous changes, and sensory decline is almost inevitable. Vision and hearing are two senses that significantly affect how we experience the world. Even mild impairment can have profound consequences.
- Safety: Poor vision or hearing can increase the risk of accidents, such as falls, or missing important auditory cues like alarms or traffic sounds.
- Social Interaction: Hearing and vision difficulties can lead to isolation, making it harder to engage in conversations or participate in activities.
- Mental Health: Sensory impairments are linked to cognitive decline, depression, and anxiety.
- Independence: Routine tasks like reading, driving, or watching television become challenging, impacting daily life.
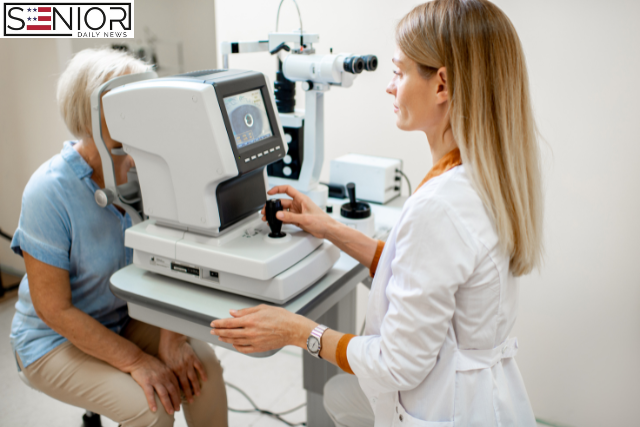
The Case for Regular Vision Tests
Many eye conditions become more prevalent with age:
- Presbyopia: Difficulty focusing on close objects, typically starting in the 40s or 50s.
- Cataracts: Clouding of the eye lens, which can blur vision.
- Glaucoma: Increased pressure in the eye, potentially damaging the optic nerve and causing vision loss.
- Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD): Loss of central vision, making it hard to read or recognize faces.
- Diabetic Retinopathy: Damage to the blood vessels in the retina from diabetes.
Benefits of Regular Eye Exams
- Early Detection: Identifying issues early allows for timely treatment, which may slow or prevent vision loss.
- Prescription Updates: Ensure glasses or contact lenses are current for optimal vision.
- Monitoring Chronic Conditions: Conditions like diabetes and hypertension can be monitored through eye health.
- Eye Health Maintenance: Preventative care can help reduce the risk of severe issues.
The Case for Regular Hearing Tests
Hearing loss affects approximately one-third of people over 65. Common age-related hearing problems include:
- Presbycusis: Age-related hearing loss, usually affecting both ears.
- Tinnitus: Ringing or buzzing in the ears.
- Conductive Hearing Loss: Blockages or damage to the ear canal or middle ear.
Benefits of Regular Hearing Tests
- Improved Communication: Identifying hearing loss can lead to interventions like hearing aids, improving social interactions.
- Mental Health Protection: Reducing isolation and cognitive decline associated with hearing impairment.
- Safety: Ensures seniors can hear alarms, emergency signals, and conversations.
- Quality of Life: Enhances the ability to enjoy activities like music, television, and phone calls.
What to Expect During Vision and Hearing Tests
Vision Testing Procedures
- Visual Acuity Test: Measures how clearly you see at various distances.
- Tonometry: Checks for glaucoma by measuring eye pressure.
- Retinal Examination: Looks at the back of the eye for signs of damage.
- Refraction Test: Determines prescription for glasses or contact lenses.
Hearing Testing Procedures
- Pure-Tone Testing: Determines the faintest tones you can hear at various pitches.
- Speech Recognition Tests: Measures ability to understand speech.
- Tympanometry: Examines the middle ear function.
- Otoacoustic Emissions (OAEs): Tests inner ear response.
Encouraging Seniors to Get Regular Screenings
Seniors may avoid vision and hearing tests for various reasons, including denial, fear, or cost concerns. Family members and caregivers play a vital role in encouraging regular check-ups.
- Educate on Importance: Explain how sensory health impacts overall well-being.
- Make It Routine: Incorporate tests into annual health check-ups.
- Address Concerns: Reassure them about the simplicity and painlessness of the procedures.
- Seek Financial Assistance: Many programs and insurance plans cover routine screenings.
FAQs About Vision and Hearing Tests for Seniors
Q: How often should seniors have vision and hearing tests? A: Generally, seniors should have annual eye exams and hearing tests every 1-3 years unless otherwise recommended by their healthcare provider.
Q: What are signs that a senior may need a vision or hearing test? A: Difficulty seeing or hearing clearly, frequent misunderstandings, turning up volume excessively, or withdrawing from social activities.
Q: Are vision and hearing loss inevitable in old age? A: While common, not all seniors experience significant loss. Regular testing and care can minimize impact and preserve abilities.
Q: What treatments are available if issues are detected? A: Glasses, contact lenses, surgeries (like cataract removal), and hearing aids or cochlear implants can significantly improve quality of life.
Q: Do Medicare or insurance plans cover these tests? A: Coverage varies. Many plans include preventive vision and hearing services, but always check specific plan details.
Image Designed Using Canva